Extended Reality: Key details that you need to know
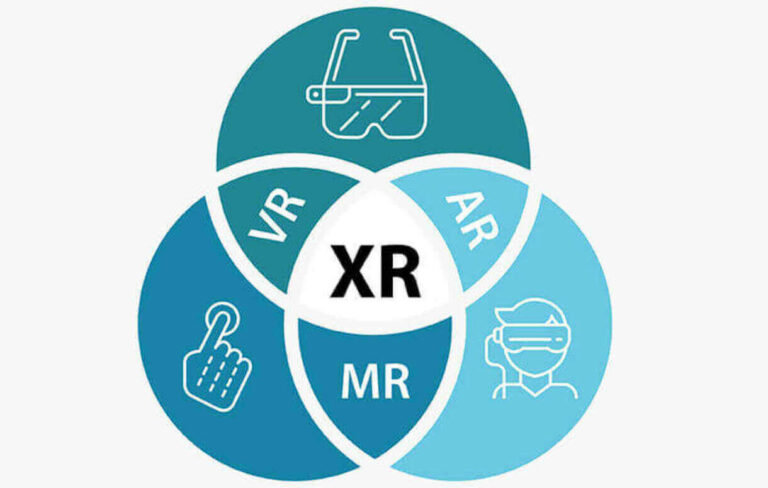
Extended Reality or XR is an umbrella term that is used to describe the different similar technologies of Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR).
These extended reality technologies merge the physical and virtual worlds to create new environments with new experiences and interactions for the user. It is in a way, an extension of the the physical world – and hence the term “Extended Reality”.
This post looks at the benefits and applications of extended reality for business and pleasure. As well as future implications of the technology for various industries.
The Extended Reality Trend
Extended reality combines similar technologies of virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality into one term for easy reference. All 3 technologies approach spatial computing from different angles while trying to provide the best value for users.
The extended reality market is expected to grow at a CAGR (Compounded Annual Growth Rate) of 34.94% from $105.58 billion in 2023 to $472 billion by 2028. The key drivers of this market growth include the rising adoption of VR and AR technologies, as well as the increasing use of connected devices and smartphones by more market players.
The Different Types of XR
Three similar but different technologies combine to make up extended reality. Each one comes with its pros and cons, which either make it more or less ideal for specific situations. Here is a closer look at these 3 extended reality types.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Virtual reality technology offers the user an environment that is completely virtual and immersive. Thus, the user is transported into a different reality, the moment he/she puts on a VR headset. Virtual reality cuts users off completely from the physical world around them. They are used for simulations, training, gaming, and entertainment.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Augmented reality uses virtual content to improve the real world. So, an AR user basically sees his/her physical environment, but with digital information overlaid on some areas or physical objects. Augmented reality is available on headsets and with mobile phones and tablets. It is used for navigation, gaming, and different types of information display projects.
- Mixed Reality (MR): Mixed reality is a more advanced technology that combines elements of virtual reality and augmented reality. It merges a user’s real and virtual elements to create a hybrid environment where virtual objects can interact and respond to the physical environment. MR is used for design visualizations, collaborative work, training projects, and other complex simulations.
Benefits of Extended Reality
Extended reality offers many benefits across different industries and applications. Here are some of the key ones.
- Enhanced User Engagement: The immersive experience that extended reality offers, enables its users to feel as part of the environment and thereby boost their interactions with the system on all levels.
- Enhanced Learning – Extended reality’s immersive experience also boosts users’ learning capabilities, leading to its use in education, medical training projects, job training, and simulations of risky situations.
- Lower Costs: The ability to simulate scenarios virtually can help organizations save the costs of physically building product prototypes or having employees travel from one place to another for training.
- Anti-phobia Therapy: XR systems can help phobia sufferers challenge their fears without having to physically put themselves in danger of whatever it is that they fear.
- Improved Designs: Designers and architects can visualize their designs better in 3D reality to make improvements and increase the value of their work.
- New Innovation: Developers can utilize the new opportunities offered by extended reality and its emerging technologies to develop services or products that add value to user’s lives – and probably start new ventures.
- Real-time Data Overlays: The ability to overlay relevant information on physical objects opens many doors for individualized applications from tourism to gaming, shopping, and so on.
Challenges of Extended Reality
As is expected from most technologies and their development, extended reality comes with challenges that reduce its appeal for various applications. Here are the key challenges.
- Hardware Costs: High-quality XR hardware can be relatively expensive. So, while you can get a good computer for a few hundred dollars, good XR hardware costs several thousand dollars. But with mass production, they might get cheaper in the future though.
- Design Challenges: Unlike the standard display in most computers, the display possibilities in extended reality are nearly endless, and this brings problems of its own. Each developer or company is coming up with a unique design and display approach, so it might still be a while before industry standards evolve.
- Location Privacy: Since many extended reality applications rely on the user’s location to function, location privacy becomes a design issue that bad actors can take advantage of.
- Bandwidth: Depending on the type of application, extended reality can be bandwidth intensive, as you need lots of data to create and recreate 3D environments.
- Ethical Concerns: Issues like addiction and the potential to manipulate or misinform a user are some of the ethical concerns in relation to extended reality.
Applications Of Extended Reality
Extended reality technology finds application in numerous industries by leveraging the capabilities of both real and virtual worlds and their objects to create new opportunities for human interaction and work.
- Gaming & Entertainment: Virtual reality and augmented reality technologies offer vast options for games. From augmented real-world experiences with location-based games like Pokémon GO to fully virtual reality games like Half-Life.
- Education & Training: Extended reality also offers many education and training options, including interactive simulations, training scenarios, and virtual field trips. This enables industrial workers, for instance, to learn and practice complex or dangerous tasks in a safe environment. The same goes for medical students who can safely practice surgeries and military personnel who can practice with the latest weapons technologies.
- Healthcare: Extended reality applications can help in patient education and rehabilitation, as well as in training for medical professionals.
- Architecture: Architects, interior designers, and urban planners can create immersive experiences of their projects that allow clients to get a virtual walk-through before physical construction begins.
- Design & Engineering: From prototyping to training sessions, XR systems can equally aid manufacturers in designing and engineering products.
- Retail & E-commerce: Shopping systems can equally be improved by different extended reality applications. From AR information overlays on physical shop products to virtual try-ons, shop navigation using AR, furniture placements to help intending buyers visualize, interactive catalogs and packaging, and other extended reality experiences that can help boost customer experience and sales.
Extended Reality Accessories
The quality of an extended reality experience depends on the accessories in play, as various sensors and devices can enhance the immersion, interaction, and functionality of the system. Here are some of the major extended reality accessories.
- Headgear: These include the display, speakers, motion, and other attachments worn around the head. Most XR headgear is unique and easily identifiable from others.
- Haptic Feedback: Bodysuits and other devices that allow users to feel virtual objects on their bodies.
- VR Controllers: Devices that enable the user to navigate the virtual reality space around them. This often includes handheld devices but can also be integrated into the headgear.
- Locomotion Devices: Some XR systems involve the user moving around a lot and can come with specialized platforms, such as treadmills to make such physical locomotion easier.
- Aim Controllers: Shooter games often include physical gun devices to create more realistic aiming and shooting experiences.
- Hand Tracking: Hand tracking makes it easy for the system to follow and understand the user’s hand gestures as a method of controlling the computer and the entire environment. Hand tracking removes the need for physical controllers.
- Eye Tracking: Extended reality systems can also track the user’s eye to render quality graphics in the direction that he/she is looking. As this improves the experience.
- Body Tracking: A body tracking system tracks the user’s body movements to provide a better virtual representation.
- External Tracking: These are any additional sensors that are installed in any area of the room, so they can capture user movements with better precision.
Extended Reality FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about extended reality.
Q: What are the differences between XR, VR, AR, and MR?
A: VR or Virtual Reality creates a completely virtual and immersive environment, while AR or Augmented Reality overlays digital objects and information in the real world, and MR or Mixed Reality combines elements of VR and AR while allowing virtual objects to interact with the real world. XR or Extended Reality is an umbrella term for them all.
Q: Does XR require specialized hardware?
A: Yes and no. Most XR applications require specialized headsets and other accessories. But it’s still possible to experience XR with just a smartphone.
Q: Are there future business opportunities in extended reality?
A: Yes, aside from remote collaborations, games, and product development, there’s still the possibility of more innovations around this technology.
Q: Is extended reality safe?
A: Extended reality is generally safe for average users. However, prolonged use can lead to motion sickness and related conditions.
Q: Why is extended reality important?
A: Because it opens up new areas for research and development of human-computer interactions.
Conclusion
Wrapping up this blog about extended reality and its related technologies, you have seen how augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality are creating new markets and opportunities.
While the future and how things will play out remain speculations, the benefits of enhancing our physical reality with digital elements to create an extended reality that boosts productivity and entertainment are already overwhelming.